Newer Surgical Techniques Around the Horizon

Dr Maya Hada, MD
Assistant Professor, SMS Medical
College & Hospital, Jaipur
Oculoplastic surgery largely consists of traditional surgical approaches with archaic surgical instruments, but advances in both surgical and non-surgical approaches to functional and aesthetic oculoplastic surgery are continuously being made. There has been a trend for more minimally invasive procedures, that are rapidly changing the oculoplastics landscape. This article discusses some of these trends and newer techniques in oculoplastic surgery around the horizon.
Orbital surgeries
Newer technologies such as ultrasonic bone emulsification and intraoperative CT/MRI image guidance systems in orbital surgeries, allow to perform more effective surgeries and achieve a higher level of safety during surgery for the patient at the same time.
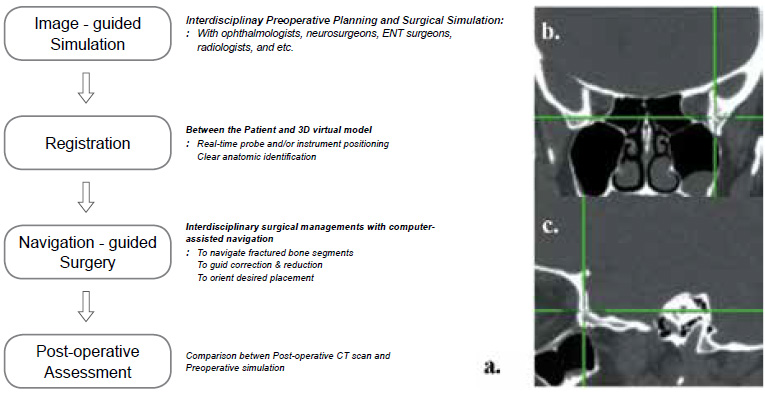
Figure 1: Stereotactic probe assisted intraoperative localization.
a. Flow diagram showing interdisciplinary surgical management with image-guided navigation. Tip of the probe is placed at posterolateral orbital wall.
b. Coronal view shows the vertical and lateral location of the probe tip while the tip of the probe is placed at posterolateral orbital wall.
c. Saggital view demonstrates anteroposterior and vertical depth of the probe tip with respect to posterioe wall.
Stereotactic image guidance in orbital surgery
Image guidance has been used in neurosurgery with great success. The appreciation of lesion disposition and morphology in 3-dimensional space using frameless stereotactic technology has been introduced in the field of orbital surgery [1]. Based on preoperative imaging, selected points on the patient’s scalp are coregistered with the image space using a probe with a light-emitting diode. In this way, the tip of the probe can be used intraoperatively to effect real-time correlation between anatomical structures and their corresponding sites on the preoperative imaging studies (Fig.1).
Orbital wall decompression in thyroid eye disease also utilizes the intraoperative CT-image-guidance system for better localization during surgery. Use of an ultrasonic bone emulsification system [2], which uses piezoelectric technology, preferentially emulsifies the immobile bone tissue over the more pliable soft tissue. It optimizes the bony decompression while preventing inadvertent soft tissue trauma, thus maintaining the safety of the anterior and middle cranial fossae dura. Application of this relatively new technology to orbital surgery has improved both surgical efficacy and safety.
Aesthetic surgeries
1. Blepharoplasty Blepharoplasty surgery in present scenario is more than just excising fat or skin. It aims to restore the entire mid-face structure. Blepharoplasty of the lower eyelid has always presented a challenge due to the problem of the post-blepharoplasty syndrome with lower lid retraction and a hollowed look. New techniques that reposition fat over the inferior orbital margin, avoiding the removal of fat have improved the outcomes. The ‘tear trough’ defect of the lower eyelid can be addressed at the same time combining the procedure with an orbicularis suspension technique or a mid-face lift.
CO2 laser application in conjunction with incisional upper blepharoplasty was described by Kotlus et al [3]. the laser was applied to the subbrow skin, the upper medial canthal skin and the pretarsal skin a reduction in rhytidosis was demonstrated. The authors conclude that the results reduce the need for medial incisions to address medial canthal, upper eyelid/infra-brow skin redundancy and rhytides of the medial canthus and upper eyelid.
Combining Z-epicanthoplasty and blepharoplasty is described by Zhao et al [4], to develop outfold type double eyelids for Asian blepharoplasties. The upper eyelid blepharoplasty incision is extended toward the crossing point of the epicanthal vertical axis and the lower eyelid skin. An additional line is drawn from the upper skin incision to the new intended point of the medial canthus. Two flaps are made and transposed to reform the medial canthus, obliterating the epicanthal fold and exposing the caruncle.
2. Brow Lift Surgery
Present approaches to brow lift surgery include a direct brow lift with incision just above the brow hair, a pretrichial brow lift with the incision just anterior to the hairline, a coronal brow lift with an ear-to-ear incision behind the hairline, and an endoscopic brow lift with small incisions hidden behind the hairline. Transblepharoplasty Endotine fixation [5] : A new, absorbable Endotine transblepharoplasty fixation device holds promise to improve postoperative results as compare to standard internal browpexy (Fig.2)
Minimal incisions vertical endoscopic lifting (MIVEL) :
Bernardini et al described this approach combined with fat grafting to optimize rejuvenation of the periocular aesthetic unit [6]. In this technique, a Gennai stitch is used by making stab incisions in the forehead just below the paramedian incisions. A Reverdin needle is passed from the forehead incision under the scalp to exit at the paramedian incision. The needle is loaded with the suture and brought back out of the forehead incision. The suture
repositions the deep tissues to a more posterior location.
Small-incision frontalis muscle transposition flap :
Costin and Perry described this technique recently for lateral eyebrow ptosis repair [7]. A 1.5 cm incision is made in a lateral forehead rhytid. Dissection is carried down to expose the frontalis-orbicularis angle, the frontalis-orbicularis insertion and the lateral extent of the frontalis muscle. A pedicle of frontalis muscle is then created
and transposed laterally to lift the brow.
Blepharoptosis Repair
Levator advancement and conjunctival-mullerectomy surgeries are the most popular methods to raise eyelids that have good levator function. Small incision levator advancement, and the levator aponeurectomy is described by John Martin [7]. In this technique, through the traditional blepharoplasty incision, the septum is incised and the levator aponeurosis and muscle are exposed. A small rectangle of orbicularis and levator aponeurosis at the superior edge of the tarsus is removed. The cut edge of the levator is then advanced to the lower edge of the subcutaneous deep tissues, thereby advancing the central portion of the levator and effectively raising the lid.
Conjunctiva sparing posterior ptosis surgery:
Vrcek et al published this technique, in which conjunctival excision was not performed with muller’s resection [8] . This technique allows conservation of anatomically normal tissue, retention of goblet cells, and reduction of suture related complications such as corneal irritation or abrasion.
Ectropion Repair
Transposition of corrugator supercilii muscle-tendon unit flap for contralateral paralytic medial ectropion repair is recently described by Genther et al [9]. This study was done in cadavers, so was preclinical and aimed to demonstrate
the reasonable feasibility of flap dissection and transposition, as well as the adequacy of length of the corrugator supercilii muscle flap.
Laser treatment of cicatricial ectropion:
Treatment of cicatricial ectropion secondary to burns, trauma, and post eyelid reconstruction, with the use of ablative fractional laser resurfacing on the scar area, followed by topical 5-FU with or without steroids appears promising as has shown significant improvement in the tone of the skin and position of the eyelid.
Entropion Repair Lid crease approach to upper eyelid margin rotation [10] :
Antonio Cruz et al proposed this approach, which allows the surgeon to simultaneously address other common lid problems, such as dermatochalasis, retraction and ptosis, with the advantage of the sutures to be buried beneath the skin, obviating the need to externalize the sutures and use bolsters. A typical lid crease incision is made and the anterior lamella is dissected off of the tarsal plate. Then a full thickness incision is made parallel to the lid margin about 3 mm above the lash line and the distal portion of the tarsus to be advanced over the marginal tarsus and correcting the abnormal eyelid position.
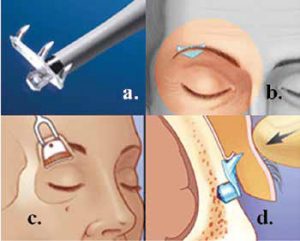
Figure 2: Endotine transblepharoplasty brow fixation system.
a. Endotine implant with inserter.
b. Endotine and brow position after implantation.
c. Location of osteotomy over orbital rim.
d. Tissue fixation onto Endotine implant
Shared buccal mucosal graft :
Mancini and Kerr recently described a technique of simultaneous repair of severe upper and lower eyelid cicatricial entropion, with the use of shared buccal mucosal graft [11]. The shared mucosal graft was split one week post operatively. The new oculoplastic surgical techniques and the modifications of older procedures, have enabled the
ophthalmoplastic surgeons to achieve better results. These aim to improve patient outcomes while at the same time adhering to the sound surgical and medical principles according to anatomy.
References
1. Lee KY, Ang BT, Ng I, Looi A. Stereotaxy for surgical navigation in orbital surgery. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009 Jul- Aug;25(4):300-2.
2. Vrcek I, Starks V, Mancini R, et al. Use of an ultrasonic bone curette (Sonopet) in orbital and oculoplastic surgeryProc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2015 Jan; 28(1): 91–93.
3. Kotlus BS, et al. Upper Eyelid Fractional CO2 Laser Resurfacing With Incisional Blepharoplasty. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016 Jul-Aug
4. Zhao J, Qi Z, Zong X et al. A Modified Method Combining Z-Epicanthoplasty and Blepharoplasty to Develop Out-Fold Type Double Eyelids. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2016 Feb;40(1):48-53
5. Langsdon PR, Williams GB, Rajan R et al. Transblepharoplasty brow suspension with a biodegradable fixation device. Aesthet Surg J. 2010 Nov-Dec;30(6):802-9
6. Bernardini, Francesco P, Gennai et al. Minimal Incisions Vertical Endoscopic Lifting and Fat Grafting as a Systematic Approach to the Rejuvenation of the Periocular Esthetic Unit. Ophthalmic Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery. 2013 Jul- Aug 29(4):308-315.
7. Costin BR, Perry JD. Smallincision frontalis muscle transposition flap for lateral eyebrow ptosis repair. Ophthal
Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015 Jan- Feb;31(1):63-5.
8. Vrcek I, Hogan RN, Rossen J et al. Conjunctiva-Sparing Posterior Ptosis Surgery: A Novel Approach. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016 Sep-Oct;32(5):366-70.
9. Genther DJ, Kim LR1, Loyo MD et al. Transposed Corrugator Supercilii Muscle-Tendon Unit Flap for Contralateral Paralytic Medial Ectropion Repair. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2016 May 1;18(3):231-2.
10. Cruz AA et al. The Versatile Lid Crease Approach to Upper Eyelid Margin Rotation. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2015 Oct- Dec;22(4):407-9.
11. Kerr T, Mancini R. Shared buccal mucosal graft for simultaneous repair of severe upper and lower eyelid cicatricial entropion. Orbit. 2016;35(1):24-8.