Disc Drusens: Not all that benign
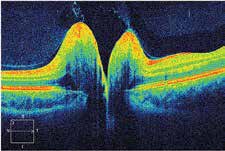
Monteiro MLR et al reported two cases of disc drusen causing sudden vision loss and mimicking optic neuritis. Sudden visual loss and optic disc edema caused by optic neuritis (ON) is usually followed by significant visual recovery. However, little or no recovery occurs when the loss is caused by atypical ON, especially in patients with neuromyelitis optica (NMO). Optic disc drusen (ODD) is a cause of pseudo optic disc edema and may be a predisposing factor for non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), thereby mimicking atypical ON. In such cases, if globular concretions are seen protruding from the disc substance, ODD may be suspected. The purpose of this paper is to describe two patients with acute visual loss followed by optic disc atrophy initially labeled as atypical ON. Though not suspected on clinical examination, optical coherence tomography (OCT) revealed deeply buried ODD as a predisposing factor for NAION.
The first case is of a 48-year-old woman who had bilateral sequential visual loss associated with optic disc edema. Despite treatment, vision did not improve and severe disc pallor ensued. Atypical ON was suspected. Eventually, she was started on immunosuppressant therapy based on a tentative diagnosis of NMOspectrum disorder. On examination 5 years later, only severe optic disc pallor was observed, but OCT radial B-scans showed ovoid hyporeflective areas in the retrolaminar region of both eyes, compatible with ODD; this led to a diagnosis of NAION and deeply buried ODD. The second case is of a 35-year-old woman with suspicion of ON in the left eye and a history of previous atypical ON in the right eye was referred for neuroophthalmic examination which revealed diffuse optic disc pallor and a dense arcuate visual field defect in the right eye. OCT B-scans passing through the disc showed large ovoid areas of reduced reflectivity in the retrolaminar region of the optic disc in the right eye. These findings helped confirm the diagnosis of NAION in one eye, with deeply buried ODD as predisposing factor.
The authors concluded that deeply buried ODD may be associated with NAION causing irreversible visual loss and optic disc pallor, a condition easily mistaken for atypical ON. Awareness of such occurrence is important to avoid unnecessary testing and minimize the risk of mismanagement
Read More:
Monteiro MLR et al. Acute visual loss and optic disc edema followed by optic atrophy in two cases with deeply buried optic disc drusen: a mimicker of atypical optic neuritis. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018 Oct 26;18(1):278.
Use OCT to help confirm papilledema
Carta et al assessed the usefulness of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness measurement in discriminating early phase optic disc edema (ODE) from pseudoedema (PODE). They conducted a hospitalbased, multicenter, cross-sectional study involving external patients referred for recent identification of “presumed ODE”. Patients underwent SD-OCT optic nerve head (ONH) RNFL thickness measurement at their first evaluation. In 155 of these, the causative etiology was subsequently ascertained and the respective eyes (one per patient) were assigned to the ODE (95 eyes) or PODE (60 eyes) group. Admission SD-OCT data were retrieved and used for the analysis. ROC curve analysis was used to calculate specificity, sensitivity and predictive value (PV) of the RNFL values. The PODE group was significantly younger than the ODE group (p = 0.007). The average and any single-quadrant RNFL thickness was significantly higher in the ODE group compared with the PODE and control groups. The average and the inferior quadrant thicknesses tested the most powerful parameters to differentiate ODE from PODE. A cutoff value of ≥ 110 μm for the average area, or of ≥ 150 μm for the inferior quadrant was associated with maximal sensitivity and specificity with positive PV greater than 80%. The authors concluded that the SD-OCT evaluation of the peripapillary RNFL achieved good specificity, sensitivity and positive PV in discriminating between ODE and PODE. Despite the correct differential diagnosis between these categories still relies on a careful medical history taking and other ancillary testing, we proved the usefulness of SD-OCT RNFL measurement in supporting the
diagnostic process.
Read More:
Carta A et al. Optical coherence tomography is a useful tool in the differentiation between true edema and pseudoedema of the optic disc. PLoS One. 2018 Nov 29;13(11):e0208145.