True robotic surgery in ophthalmology
In a first of a kind study, Chammas J et al performed robot-assisted penetrating keratoplasty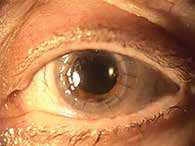 (PK) using the new Da Vinci Xi Surgical System and demonstrated successful use of this system in experimental eye surgery. Robot-assisted PK procedures were performed on human corneal transplants using the Da Vinci Xi Surgical System. For each eye an 8-mm corneal trephination was done and 4 interrupted and 1 10.0 monofilament running sutures were placed. Robotassisted PK was successfully performed on 12 corneas. The Da Vinci Xi Surgical System proved to be dexterous for the surgery and completed the procedures in ½ to 1 hour. Postoperative SDOCT confirmed that the sutures were placed at the appropriate depth. They recommended further experiments with the system.
(PK) using the new Da Vinci Xi Surgical System and demonstrated successful use of this system in experimental eye surgery. Robot-assisted PK procedures were performed on human corneal transplants using the Da Vinci Xi Surgical System. For each eye an 8-mm corneal trephination was done and 4 interrupted and 1 10.0 monofilament running sutures were placed. Robotassisted PK was successfully performed on 12 corneas. The Da Vinci Xi Surgical System proved to be dexterous for the surgery and completed the procedures in ½ to 1 hour. Postoperative SDOCT confirmed that the sutures were placed at the appropriate depth. They recommended further experiments with the system.
Read More:
Chammas J, Sauer A, Pizzuto J, Pouthier F, Gaucher D, Marescaux J, Mutter D, Bourcier T Da Vinci Xi Robot-Assisted Penetrating Keratoplasty. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2017 Jun 20;6(3):21.
Oral Voriconazole Versus Oral Ketoconazole in Fungal keratitis?
A randomized control trial was conducted to evaluate the use of oral voriconazole or oral ketoconazole in addition to topical natamycin for fungal keratitis. The study enrolled 50 eyes of 50 patients of proven fungal keratitis. They were randomized to receive either oral oral voriconazole or oral ketoconazole 200 mg twice a day in addition to topical natamycin. Three months follow up was done to evaluate best spectacle-corrected visual acuity, percentage of healed cases and scar size. The study found that although the duration and percentage of healing was similar in both groups, oral voriconazole attained a significantly better tear film concentration with a smaller scar size and better best spectacle-corrected visual acuity compared with oral ketoconazole. The authors recommended voriconazole in severe fungal keratitis
Read More:
Sharma N, Singhal D, Maharana PK, Sinha R, Agarwal T, Upadhyay AD, Velpandian T, Satpathy G, Titiyal JS. Comparison of Oral Voriconazole Versus Oral Ketoconazole as an Adjunct to Topical Natamycin in Severe Fungal Keratitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Cornea. 2017 Sep 8.
Infantile Corneal trauma in India
Ophthalmologists are often faced with parents bringing infants with red eye and a history of ocular trauma. A retrospective study on corneal trauma in infants (≤12 months old) was published recently and evaluated the clinical profile, etiology, microbiological profile, clinical course, and outcome of ocular trauma. Seventy-six infants were included and nearly 70% presented within the first 24 hours of trauma. Infants presented with inability to open the eyelids, redness of eyes, and watering. Self-infliction by child’s hand (49%) was the commonest cause. Majority presented with corneal abrasion (45%), isolated epithelial defects (30%), and infective keratitis (25%). A good thing noticed in the study was that patients presented early but there was a high loss to follow-up.
Read More:
Shah VD, Uddaraju M, Singh A, Das RR. Clinical Profile, Etiology, and Outcome of Infantile Ocular Trauma: A Developing Country Perspective. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2017 Jun 20.